Osmosis In An Animal Cell
Osmosis is the move of solvent molecules from solution of low concentration to solution of loftier concentration, through a semipermeable membrane. Two types of osmosis are Endosmosis and Exosmosis. Osmotic solutions can be isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic. Osmotic pressure ceases the water from diffusing through the membrane. Osmosis maintains the level of water and other cellular fluids in living organisms.
Key Terms: Osmosis, Osmotic Solution, Osmotic Pressure, Exosmosis, Endosmosis
Read about: Contrary Osmosis
Introduction to Osmosis
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane, from the solution of low concentration to the solution of high concentration. Molecules move from high concentration to low concentration. The process ends when concentrations on both sides of the membrane become equal. Osmosis does non require use of energy.
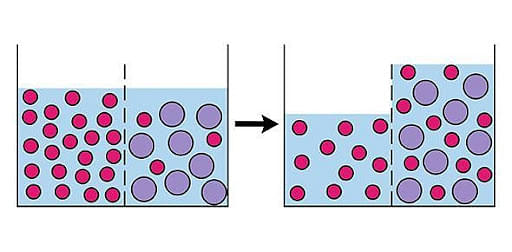
Osmosis
As well Read: Electroosmosis
Osmotic Solutions
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The iii types of osmotic solutions are Isotonic, Hypertonic, and Hypotonic.
a) Isotonic Solution: The solution in which cells accept the same concentration of solutes, both inside and outside, is an isotonic solution.
b) Hypertonic Solution: The solution in which solute concentration is college on the exterior is called hypertonic solution.
c) Hypotonic Solution: The solution in which solute concentration is college on the inside is called hypotonic solution.

Osmotic Solutions
Types of Osmosis
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
In that location are ii types of osmosis: Endosmosis and Exosmosis.
a) Exosmosis: Exosmosis involves the use of hypertonic solution. The substance is placed in the solution, due to which the solvent molecules get-go moving exterior the prison cell. This leads to the cell going through the process of plasmolysis.
b) Endosmosis: Endosmosis involves the use of hypotonic solution. The substance is placed in the solution, due to which the solvent molecules first moving inside the jail cell. This leads to the jail cell going through the process of deplasmolysis.
Also Read: Reproductive Wellness
Osmotic Pressure level
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The pressure required to end the procedure of osmosis is osmotic force per unit area. Osmotic pressure ceases the h2o from diffusing through the membrane. The water travels from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration until the concentration is equal on both sides.
Osmotic pressure is the product of temperature, tooth concentration, and gas constant.
Osmotic Pressure level = Chiliad x R ten T
In the above equation, M denotes molar concentration, R denotes abiding, and T denotes the temperature.

Osmotic Pressure
Importance of Osmosis
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
- Osmosis helps go on the cells turgid.
- Diffusion of h2o in cells is controlled through osmosis.
- Osmosis prevents drought injury in plants past building high osmotic pressure level.
- Dehiscence of sporangia is controlled past osmosis.
- The transport of nutrients in plants is aided by osmosis.
- Plants release the metabolic waste matter products through osmosis.
- Osmosis helps plants in maintaining their water content.
- Osmosis helps plants in arresting water from the soil and transporting it throughout the plants.
- Osmosis maintains the level of water and other cellular fluids in living organisms.
Read More: Heterotrophic Bacteria
Osmosis on Cells
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Osmosis affects animal cells and plant cells differently.
When placed in a hypotonic solution, an animal cell undergoes lysis. The plant cells undergo no such harm due to hypotonic solution. This is considering a plant cell requires more water to seep through its thick walls. Then, plant cells should ideally be placed in a hypotonic solution. Use of isotonic solution for constitute cells leads to loss of turgidity. An isotonic solution is platonic for fauna cells.
Also Read: Jail cell Wall and Cell Membrane
Things to Remember
- Osmosis refers to the process of motility of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane, from the solution of low concentration to the solution of high concentration.
- The 2 types of osmosis are Endosmosis and Exosmosis. Endosmosis involves the use of hypotonic solution whereas exosmosis involves the apply of hypertonic solution.
- The 3 types of osmotic solutions are Isotonic, Hypertonic, and Hypotonic.
- The solute concentration is equal on both sides of cells in isotonic solution. An isotonic solution is ideal for beast cells.
- The molecules travel from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration until the concentration is equal on both sides.
- Osmosis is important in living organisms. Osmosis helps plants in absorbing water from the soil and transporting it throughout the plants. Improvidence of water in cells is controlled through osmosis.
Likewise Read: Difference between Agile and Passive Ship
Sample Questions
Ques. What is contrary osmosis? (2 Marks)
Ans. Opposite osmosis is the procedure of filtration that is used to filter big molecules and impurities. Only pure water can pass through the semipermeable membrane used in opposite osmosis. Reverse osmosis works by reversing the process of osmosis. In reverse osmosis, pressure applied is higher than the osmotic pressure. Opposed to osmosis, reverse osmosis is an artificial process. It is often used in h2o purification systems. It removes bacteria and other impurities from h2o.
Ques. What are some examples of osmosis? (3 Marks)
Ans. Some examples of osmosis are:
Fingers get pruney when they are placed in water for a long time menses. This is because water travels and flows inside the cells.
When a fish from freshwater or saltwater is placed in water that has unlike concentrations of salt, the fish doesn't survive for long. This is due to the flow of h2o in fish cells of fish.
Osmosis helps plants in arresting water from the soil. The water flows from soil to roots of the plants as roots have college concentration.
Ques. Write a note on active transport. (2 Marks)
Ans. The procedure of motion of molecules from depression concentration area to high concentration is known every bit active transport. This process requires energy. Molecules move using the stored energy in adenosine triphosphate, with help of protein pumps. The two types of agile transport are primary active ship and secondary agile transport. In chief active send, ATP breakdown supplies energy for molecule move to take identify. In secondary active transport, electrochemical energy is used for molecule movement.
Ques. Write a notation on Passive Ship. (3 Marks)
Ans. The motion of molecules and ions inside the cell, without utilise of any external energy, is called passive send. The 4 types of passive transport are:
a) Simple Improvidence: The movement from areas of loftier concentration to low concentration is called unproblematic improvidence.
b) Facilitated Diffusion: The passive ship of molecules and ions through jail cell membrane is called facilitated diffusion.
c) Filtration: The process of separating solid, liquid, and gases is called filtration.
d) Osmosis: Osmosis is the process of movement of solvent molecules from the solution of low concentration to solution of high concentration, through a semipermeable membrane.
Ques. Write a notation on Plasmolysis. (iii Marks)
Ans. The procedure of contraction of protoplasm of a plant cell is chosen plasmolysis. Loss of water in cells leads to plasmolysis. There are two types of plasmolysis, concave and convex. The prison cell membrane starts to detach from the cell wall during concave plasmolysis.
In convex plasmolysis, the cell membrane completely detaches from the cell wall. Concave plasmolysis can be reversed whereas convex plasmolysis cannot be reversed. The process of plasmolysis takes place in three steps: Incipient plasmolysis, Evident plasmolysis, and Final plasmolysis.
Ques. What is improvidence? What are the factors affecting improvidence? (ii Marks)
Ans. Diffusion refers to the process of movement of molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Diffusion occurs in all living organisms. It is a natural process that occurs in all living organisms. Diffusion is of two types: simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Several factors affecting improvidence are particle size, temperature, expanse of interaction, and concentration gradient. Diffusion can occur in solids, liquids, also as gases.
Ques. What is difference between Endosmosis and Exosmosis? (4 Marks)
Ans. Difference between endosmosis and exosmosis:
| Endosmosis | Exosmosis |
|---|---|
| In endosmosis, the process takes place towards the within of the cell. | In exosmosis, the process takes place towards the outside of the cell. |
| Endosmosis leads to swelling of cells. | Exosmosis leads to shrinkage in cells. |
| Endosmosis involves the utilise of a hypotonic solution. | Exosmosis involves the use of hypertonic solution. |
Ques. What is the difference betwixt osmosis and improvidence? (four Marks)
Ans. Key deviation between improvidence and osmosis is tabulated below:
| Osmosis | Diffusion |
|---|---|
| Osmosis simply takes place in liquids. | Diffusion takes place in solids, liquids, and gases. |
| Semi-permeable membrane is essential for osmosis. | Semi-permeable membrane is not essential for diffusion. |
| During osmosis, particles flow in one direction. | During diffusion, particles menstruum in all directions. |
| Only solvent molecules travel from i side to another during osmosis. | All molecules travel from 1 side to another during diffusion. |
Read More:
Osmosis In An Animal Cell,
Source: https://collegedunia.com/exams/osmosis-definition-types-importance-and-solutions-biology-articleid-3377
Posted by: hinkleofue1956.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Osmosis In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment